
Get a Quote
Get a Quote and Find Services to Fit Your Needs 50000+ Satisfied Clients
5000+ Licenses & Registration
15 Branches across India
75 Years + Combined experience
Is someone stealing your brand name? If so, you need to take the right action against the Infringement of your trademark. Brand infringement is plaguing the industry right now. Unfortunately, many ignore the perks of hard work and instead choose the pass of deception – trying to pass on their trademark on their own. As a result, many businesses are either being destroyed or losing their names in the chasm of obscurity.
Such brand infringement can have a detrimental impact on your business as well if you are not careful. Therefore, there is a need for you to find trademark infringement in India. And for that, we can help you.
Before we help take action against logo infringement, let us understand its meaning. Using a brand without the permission of the registered user is brand infringement.
Trademark or TM Infringement means breaching the right to use the registered trademark of others or using someone's registered trademark without their permission.
Trademark infringement is a violation of the exclusive rights attached to a trademark without the authorization of the trademark owner or any licensees (provided that such authorization was within the scope of the license). Infringement may occur when one party, the "infringer," uses a trademark identical or confusingly similar to a trademark owned by another party about products or services identical or similar to the products or services the registration covers.
An owner of a trademark may commence civil legal proceedings against a party which the Infringement of its registered trademark. The Trademark Counterfeiting Act of 1984 criminalized the intentional trade in counterfeit goods and services in the United States.
In many countries (but not countries like the United States, which recognize common law trademark rights), a trademark not registered cannot be "infringed" as such, and the trademark owner cannot bring infringement proceedings. Instead, the owner may be able to commence proceedings under common law for passing off or misrepresentation or under legislation prohibiting unfair business practices. In some jurisdictions, Infringement of trade dress may also be actionable.
But why is trademark infringement such a big deal, and why shouldn't even the most common TM infringement be ignored? The financial strain a business name brand infringement can put on your enterprise can make it hard to cope with the losses.
When you have registered your trademark, it means that the brand name belongs to you. It also means that your brand name makes people recognize your product. In that case, if someone were to steal your brand name, then you can already guess the damage it would bring to your business:
It is your brand that your customers trust. If someone infringes on your mark to sell a subpar product, it will blemish your brand's name. It can then cause a chain reaction – lowering customer trust while eroding customer loyalty.
If you fail to file a cease and desist notice for brand logo infringement in India on time, you will end up with manipulated customers in your hand who avoid your brand. Customer trust tends to be extremely fickle. Therefore, any case of trademark name infringement drives your customers away first.
Therefore, preventing even common brand logo infringement should be at the top of your agenda when dealing with any case that comes your way.
The Intellectual Property Authority has divided trademark infringement into the following two types:
Let us understand them in detail.
 Direct Infringement
Direct Infringement
Direct Infringement of trademark is defined under Section 29 of the Trademark Act. As per this section, the conditions of trademark infringement, in this case, are as follows:
In this case, the trademark is considered infringed upon only if an unauthorized person uses the registered trademark. In other words, a person that doesn’t have permission to use the trademark. If an authorized is using the brand name, there would not be considered any case of trademark infringement in India.
Here, the trademark in usage can either be deceptively similar or identical to the existing trademark in India. The term “deceptive” means that a common customer may get confused between similar brands and may think of them as the same. Within the legal context, the word “may” is enough to prove that Infringement is possible if the brand name is too similar. Even a mere chance of misrecognition can be damaging to the brand. And thus, identical or deceptively similar trademarks fall under the direct infringement category.
All the legal trademark infringement remedies mentioned under the Direct Infringement of the trademark are only meant for a registered trademark. Thus, these rules won't be applied in the case of an unregistered trademark.
This trademark rules violation occurs when the unauthorized user leverages the trademark to sell goods and services of the class under which the trademark has been registered.
These are all direct cases of infringements. They are almost always visible and easy to go after. However, there is another class of infringement cases where the crime isn’t so direct. Such cases of referred to us as indirect trademark infringement cases in India.
Indirect Infringement of a trademark is defined in the Trademark Act 1999 as a class of Infringement where no provisions exist. The trademark registration courts rely on the universal principle to deal with indirect infringement cases. Per these principles, the infringer and the person or the body of persons that induces the Infringement are held accountable.
The following are the different aspects of indirect trademark infringement in India:
As per Section 114 of the trademark act, vicarious liability is any company committing the Act of brand logo infringement. It means that a company, as a whole, will have to take responsibility if any company member engages in brand logo infringement in India. While it would be counted as the indirect infringing of trademarks, the whole organization would have to bear the trademark infringement penalties in India.
Here are the essential elements of Vicarious liability as per the TM infringement rules:
Note: There are no exceptions to the rules. In many instances, many claims that they acted in good faith when infringing on trademarks. However, within the eyes of the government of India, those who contributed to the criminal Act held almost equal liability, regardless of how much “good faith” was there in them when they acted upon it.
Contributory Infringement refers to someone who has – directly or indirectly – contributed to the Act of Infringement. Following are the different elements of Contributory Infringement:
If you don’t want your brand to be stolen by another party, then you must any infringer face the consequences of brand logo infringement in the following ways:
Sometimes, brand infringement doesn’t happen deliberately. People sometimes have difficulty separating inspiration from copying someone in a world lacking originality. Therefore, before you take a cease and desist letter for the TM infringement approach, you must first talk to your infringers. If they are willing to stop their Act immediately and are ready to pay for any damages for trademark infringement in India, you are good to go. We mean there is no need to immediately send an infringement warning letter.
While a pacifist approach to dealing with your trademark infringer can work, most of the time, it doesn’t. When that happens, you file an initial complaint for brand logo infringement to the authorities. In most cases, it would make you deserving of quite a bit of compensation for trademark infringement in India.
If your brand holds a lot of value and even an inkling of Infringement can damage its reputation, go with the cease and desist notice for Brand Logo infringement. Just contact a lawyer, ask him for a cease and desist notice format and choose the most effective way to stop the infringer from a stop using your trademark.
If you want to take a direct, no-fluff approach toward those trying to steal your brand name, you can tap into several civil and criminal remedies for Trademark Infringement. It can lead to you getting compensation due to the damage caused by the criminal action of Brand Logo infringement in India.
Trademark Infringement can be tackled with a better preliminary injunction. You file then when you doubt that someone is violating your trademark rights. It will stop the alleged brand-name stealer for a limited period. While it won’t be a permanent solution, it will help you take the matter to court until Brand Logo infringement is prosecuted in India. However, remember that it is how to deal with alleged Brand Logo infringement. If you lose the case, it can backfire on you as well.
A permanent Injunction is the most common way to deal with the current Brand Logo infringement cases. It is effective, can stop your infringer in its tracks, and the chances for you to win them are high. However, it is costly. Depending upon the popularity of the trademark, the average cost of a trademark infringement suit format can reach dangerous proportions.
The following are the different remedies for the Infringement of trademarks in India:
Remedies are solutions to the infringement cases of unregistered and registered trademarks. It is through these trademark infringement remedies that a suit is initiated in the courts of law.
Following are the civil remedies for Trademarks Infringement that the Trademark Act, 1999 lays down:
Injunctions, whether permanent or temporary, refer to the authoritative direction of the court of law.
The aggrieved party can ask for damages for Infringement on legitimate grounds. However, it is only applicable after the infringer has ceased its operations and it is proven that the aggrieved party has suffered a loss. It is considered when calculating damages for brand logo infringement in India.
The civil remedies for Trademark Infringement handle the profit accounts and removal of products that contain infringed trademarks.
Regarding criminal remedies, the Trademarks Act of 1999 details the punishments for the Infringement of brand logos in India.
The most basic criminal action against TM infringement in India is imprisonment for six months, or, depending upon the extent of the Act, it can extend to up to 3 years.
Another section of the criminal remedies against trademark registrations states that the one who contravenes the trademark rights of another has to pay a trademark infringement penalty of 50,000 rupees.
The civil and criminal liabilities for brand logo infringement can also lead to the cease of property of the infringer to pay for the damages caused by the Infringement of the trademark.
Under the palate of administrative remedies, the following points are present:
During the trademark registration process, it is within the power of the trademark authorities to investigate the to-be-registered trademark.
To eliminate any confusion around the brand, the applicant can make changes to the registered trademark.
The authorities can check the activity – products or services – on which the infringing trademark is used before taking action.
Before taking any legal action against brand logo infringement, the applicant must consider whether there is an infringement case. Intellectual property laws can be tricky to understand; therefore, groundless threats of brand logo infringement are getting quite common. Therefore, there is a need to understand which cases should not be considered Infringement in India:
The trademark in question has not been used in any way that can damage the reputation or the distinct character of the trademark.
When the trademark registered is used to communicate product/service quality, purpose, geographical origin, time of production, or other characteristics.
To be eligible to up against brand logo Infringement, you need to come up with all the details that can back up your case. Simply put, the requirements for TM infringement are as follows:

Here is a list of documents required to fight a trademark infringement case. The applicant must make sure to keep hard as well as soft copies of these trademark infringement requirements:
All the aforementioned documents must be first certified and supervised under an adequate trademark attorney.
The following is the procedure for Brand Logo Infringement:
You can take two approaches to deal with your TM infringement case in India.
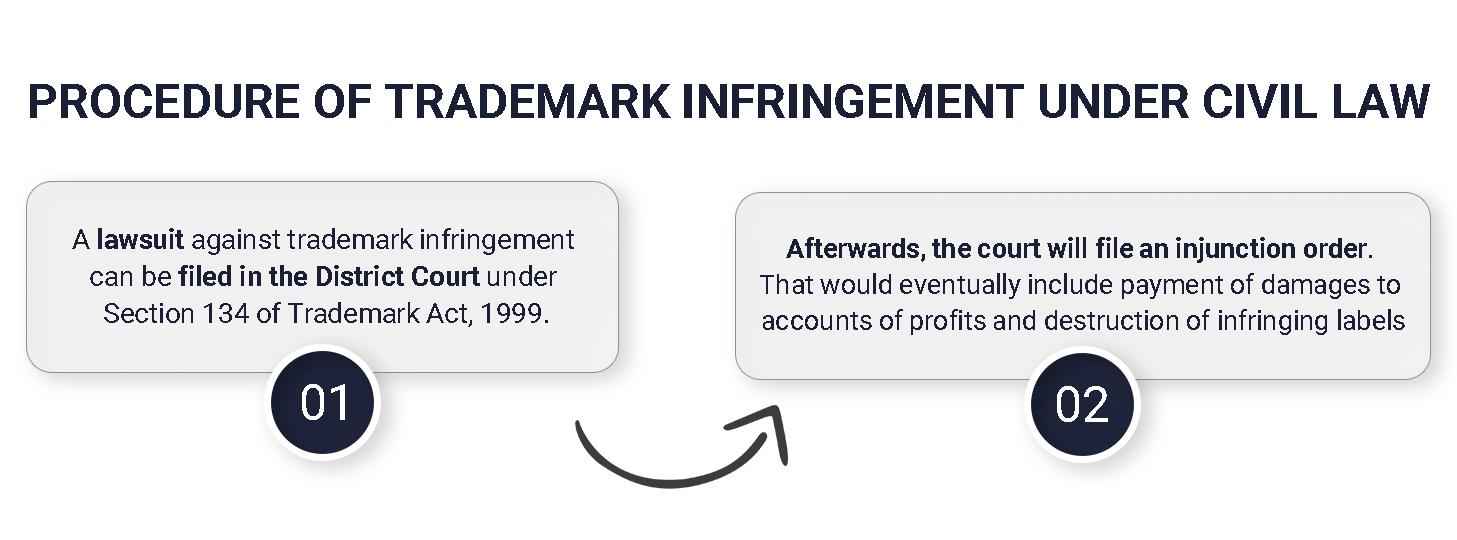
If you want to take a less vindictive approach toward the brand logo infringement case, then you must follow the specific points given below:
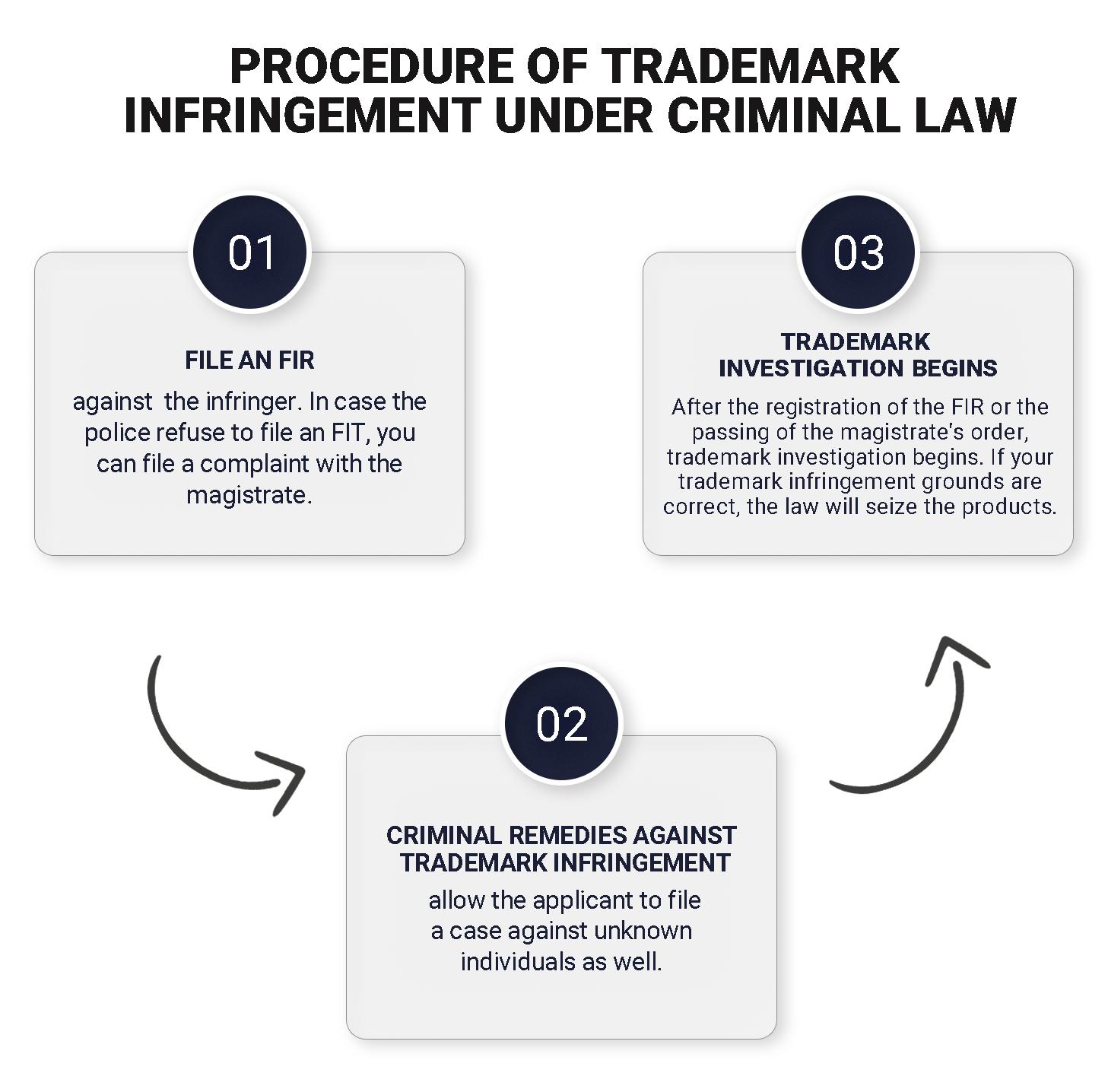 Take a more vindictive approach to deal with your infringer. You can take the following approach to deal with the criminal offence of brand logo infringement in India.
Take a more vindictive approach to deal with your infringer. You can take the following approach to deal with the criminal offence of brand logo infringement in India.
Since we have discussed much of brand logo infringement, the damages it causes to your enterprise, and the remedies that can be used in such cases, let us look at some real-life examples of brand logo Infringement cases that received national and international coverage.
Cadbury had previously registered three trademarks in India that included the name Eclairs. It even holds the right to use the shade of purple on chocolate wrappers in some regions. The three registered trademarks are for.
But Cadbury, despite being registered in 1972, didn't use any of these trademarks. So on the grounds of being latent, more than one decade later, the court announced the verdict in favour of ITC in 2015 on account of the non-usage of the registered brand name.
The plaintiff, London Dairy, which sells premium-quality ice cream, and the defendant, Londonderry, which sells inexpensive confectionery items, both of these brands sound similar phonetically, creating confusion among the customers. London Dairy stated this was a clear case of Infringement, to which the Bombay High Court disagreed because, according to the court, everything besides the sound of their brand names was different. The court held that no law says that a single pronunciation test will be sufficient to overcome all other points of differentiation. Also, there were no visual or structural similarities between their products, no similarities in colours, trade dress, goods, and pricing.
In the 1980's Bata, the shoemaker company, filed for brand logo infringement against a company for using the same brand name which sold foam materials. The court questioned the latter that a customer coming to purchase shoes would not inquire if a product is made by the shoemaker BATA. As a result, although both companies operated in distinct commercial realms, Bata, the shoemaker, won the case.
These companies provide digital payment gateways to their customers, and Paypal and Paytm target the same audience in the Indian market. But Paytm is far more popular than Paypal in the Indian market. The masses use Paytm, whereas Paypal is an internationally recognized brand whose operations in India are limited to eBay shoppers, forex investors, crypto enthusiasts, and some IT software professionals who regularly transact with the global world. Paypal's cause of worry is that if Paytm finds its place in the global market, then Paypal will lose its position and business in the global marketplace. Fearing this, in 2016, Paypal filed for brand logo infringement against Paytm for using its logo and having this homogeneity with each other's brand name. In their trademark infringement lawsuit filed in the Indian trademark office, Paypal accused Paytm of using the same two-tone colour scheme as theirs.
We at Registrationwala provide end-to-end solutions for Trademark Infringement. Our services include:
Registrationwala.com is a leading legal consultancy firm providing comprehensive services relating to Brand Logo Infringement. Contact us now if you seek us to represent you in case of Brand Logo Infringement.
Q1. What is Trademark Infringement?
A. TM Infringement is a violation of the exclusive rights attached to a trademark without the authorization of the trademark owner or any licensees (provided that such authorization was within the scope of the license).
Q2. What is common law Trademark Infringement?
A. Common law infringement factors refer to the passing of another person's trademark as your own. It is a term that mostly refers to unregistered trademarks.
Q3. What is the punishment for Trademark Infringement?
A. The common penalties for Brand Logo infringement in India are:
Q4. Where to file a Trademark Infringement case?
A. You can file Brand Logo infringement through a civil court or a police station.
Q5. How to report Trademark Infringement?
A. You can contact the police, the magistrate, or the civil court to deal with TM infringement.
Q6. How to avoid Trademark Infringement?
A. The best practices for Brand Logo infringement in India.
Q7. Where to file a Trademark Infringement case?
A. If you want to take the civil remedy route, an infringement case should be filed with the Delhi High Court. If you seek to take the criminal remedy approach, you can either reach out to the policy of the district magistrate.
Q8. How to prove Trademark Infringement?
A. You prove Brand Logo infringement by proving prior usage or that the infringing mark is either similar to or deceptively similar to yours.
Q9. Is Trademark Infringement a criminal offence?
A. Yes, Brand Logo infringement is a criminal offence in India.
Q10. What are Trademark Infringement examples?
A. Following are some of the most prominent trademark cases that will let you see things more clearly:
Q11. Who enforces Trademark Infringement laws?
A. TM Infringement is governed by the Trademarks Act of 1999 under the IP Authority of India.
Q12. Can you sue for Trademark Infringement?
A. Yes, but you must be a registered trademark owner with substantial evidence(s) of Infringement.