
Get a Quote
Get a Quote and Find Services to Fit Your Needs 50000+ Satisfied Clients
5000+ Licenses & Registration
15 Branches across India
75 Years + Combined experience
Satisfied Clients
Services
Years Combined Experience
Get Started!

























A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 which engages in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of shares, stocks, bonds, debentures, and securities issued by the Government or a local authority or other related marketable securities, leasing, hiring-purchasing, insurance or chit business.
An NBFC does not include any institution whose principal business involves any sort of agriculture activities or industrial activities or purchase or sale of any goods (other than securities) or providing any services and sale/purchase/construction of any immovable property. In order to operate as an NBFC, a company requires NBFC Registration from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Any registered company which has financial activity as its principal business must fulfill two conditions:
This test is popularly known as the 50-50 test and is applied to determine whether or not a company is in financial business. If a company fulfills both these criteria, then it will be registered as an NBFC by the Reserve Bank of India. The Reserve Bank defines the ‘principle business’ to ensure that only companies predominantly engaged in financial activity get registered with the tag of being an NBFC registration and are regulated and supervised by the bank itself.
If some companies engage in agricultural operations, industrial activity, purchase and sale of goods, providing services or purchase, sale or construction of immovable property as their principal business and are doing some financial business in a small way, they will not be regulated by the Apex Bank.
A Non-Banking Financial Company can lend credit and make investments, in the same manner as the banks, but there are a few differences that differentiate an NBFC registration from the bank in their establishment, composition and working. Some of the differences are given below:
As per the RBI Act of 1934, any Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) cannot commence or resume its business activities of operating a non-banking financial institution without
But there are exceptions to this as well. In some cases, the Reserve Bank of India has the power to obviate these dual regulations, where certain categories of NBFCs are regulated by other regulators. Therefore, they are exempted from the requirements of registration with RBI. Some examples of such financial institutions are
It is illegal for any financial entity which is an unincorporated body to make a false claim of being regulated by the Reserve Bank of India, misleading the public to collect deposits, and is liable for penalty action under the Indian Penal Code. Information in this regard may be forwarded to the nearest office of the Reserve Bank and the Police. If companies that are required to be registered with the Reserve Bank as NBFCs are found to be conducting a non-banking financial activity, such as lending, investment, or deposit acceptance as their principal business, without seeking registration, the Reserve Bank can impose a penalty or fine on them or can even prosecute them in a court of law. If members of the public come across any entity which does non-banking financial activity but does not figure in the list of authorized NBFC registrations on the RBI website, they should inform the nearest Regional Office of the Reserve Bank, for appropriate action to be taken for contravention of the provisions of the RBI Act, 1934.
To serve different purposes, the RBI has categorized and defined different kinds of Non-Banking Financial Institutions. Let us look at some of them.
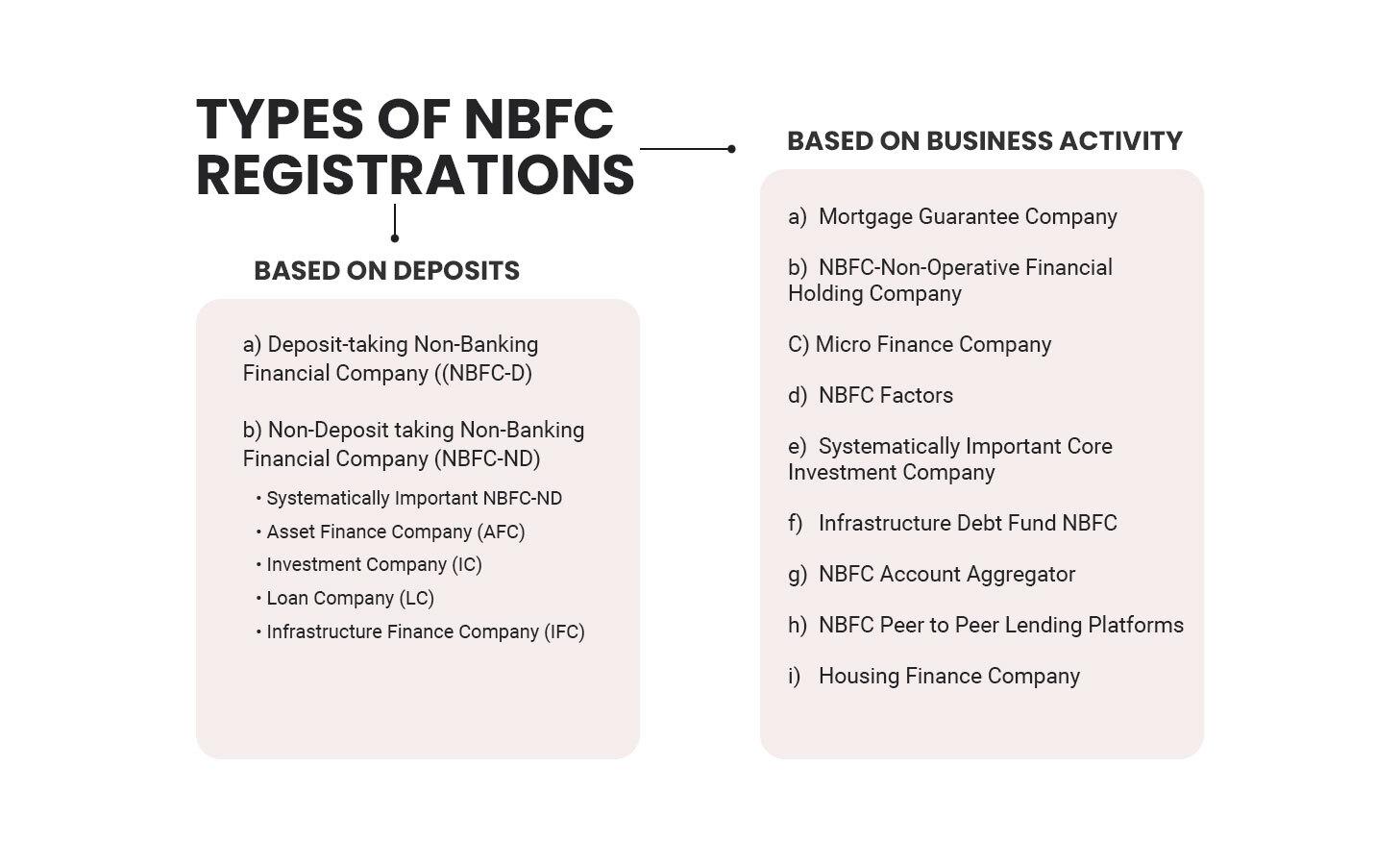
One can classify the NBFC registrations in the following ways:
Deposit-taking Non-Banking Financial Company ((NBFC-D)
Deposit Accepting NBFCs must get themselves registered with RBI as per the provisions in the RBI Act, 1934. They need a Certificate of Registration (CoR) from the RBI. And there are additional guidelines and specific regulations prescribed by RBI for them.
Non-Deposit taking Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC-ND)
Non-Deposit Accepting NBFCs also need to get registered themselves. The only difference is additional guidelines do not apply to them
Further Classification of NBFC-ND
Systematically Important NBFC-ND
NBFCs whose asset size is ₹ 500 cr or more as per the last audited balance sheet are considered systemically important NBFCs. The rationale for such classification is that the activities of such NBFCs will have a bearing on the financial stability of the overall economy.
Asset Finance Company (AFC)
The financial institution with the primary business of financing physical assets.
Investment Company (IC)
It is a financial institution engaged in the acquisition of securities as of its principal business.
Loan Company (LC)
An Institution providing finance as its principal business. The business activity is to make loans or advances or otherwise for any ventures other than its own but does not include an Asset Finance Company.
Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC)
An NBFC-IFC is a company that:
Mortgage Guarantee Company
Mortgage Finance Company is the Non-Banking Financial Company whose-
NBFC-Non-Operative Financial Holding Company
Through Non-Operative Financial Holding Company, promoter/promoter groups will be authorized to set up a new bank. It is a type of NBFC registration that will hold the bank as well as all other financial companies regulated by RBI or other financial sector regulators, to the extent allowed under the applicable regulatory prescriptions.
Micro Finance Company
Micro Finance Companies in NBFC registrations are the companies that perform the functions similar to Banks. Loans are offered by the Micro Finance companies to various small businesses that do not have access to the formal banking channels and are not eligible for availing loans. MFI shall qualify the following criteria –
NBFC Factors
NBFC-Factor is a different type of NBFC registration engaged in the principal business of factoring. The financial assets in the NBFC Factor should aggregate at least 50% of its total assets, and also income acquired from the factoring business should be at least 50% of the gross income.
Systematically Important Core Investment Company
Systematically Important Core Investment Company is a type of NBFC registration that carries on the business of share (Equity and Preference) and securities acquisition but is subject to a condition that –
Infrastructure Debt Fund NBFC
Infrastructure Debt Fund NBFC is a non-deposit-taking NBFC registration that deals in the facilitation of long-term debt into an infrastructure sector. Infrastructure Debt Fund NBFC raises the resources either through an issue of the rupee or dollar-denominated bonds of 5 years. IDF NBFCs can only be sponsored by Infrastructure Finance Company. The maturity period is of 5 years.
NBFC Account Aggregator
NBFC Account Aggregator is a new concept in NBFC registration. NBFC Account Aggregator provides data of several users and shifts their financial needs to various financial organizations. The activities of an Account Aggregator involve providing customers with financial information in a consolidated and retrievable manner to the customer. NBFC Account Aggregator provides reliable information.
NBFC Peer to Peer Lending Platforms
NBFC Peer-to-Peer lending platforms provide a platform to bring lenders and borrowers together by using a digital platform. It provides an opportunity for investors to diversify their portfolios. NBFC P2P has removed the cumbersome process of loans and has provided the ease of processing the loans. NBFC P2P Platform is the key player in the small business sector.
Housing Finance Company
Housing Finance Company is a form of NBFC registration with the principal business of financing of acquisition or construction of houses. HFCs are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. A Housing Finance company cannot commence the business without obtaining a certificate of registration (CoR) from the Reserve Bank of India.

The applicant must be an incorporated company under the Companies Act, 1956 and desirous of commencing the business of a non-banking financial institution as defined in the RBI Act of 1934 should comply with the following:
Below mentioned is the indicative checklist of the documents required to be submitted along with the application for the NBFC registration license.
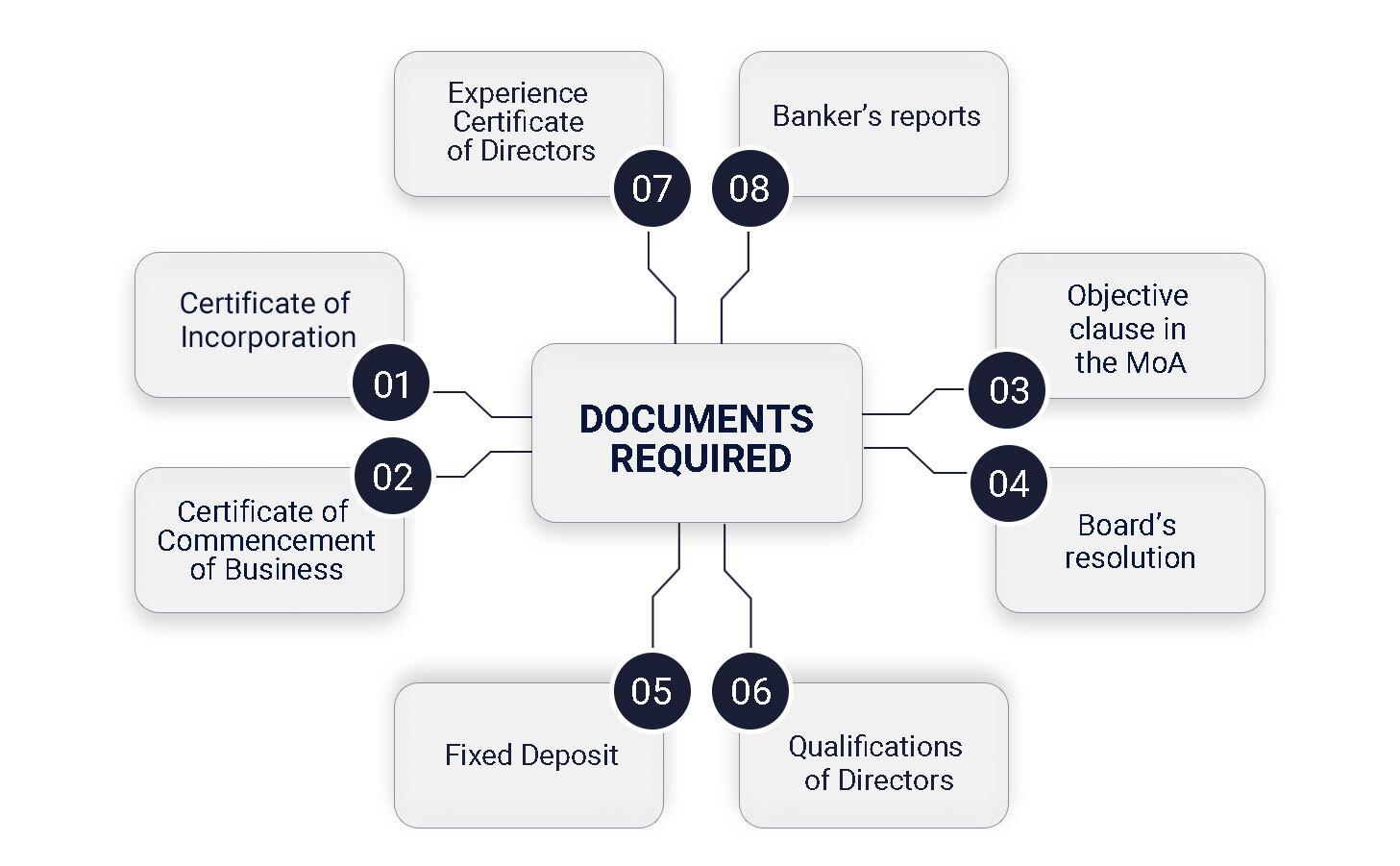
The applicant has to provide bankers' reports from all the bankers of each of these entities and provide the report for all the entities. The details of deposits and loan balances as on the date of application and the conduct of the account should be specified.
The applicant company can initiate the process of NBFC registration in the following manner:
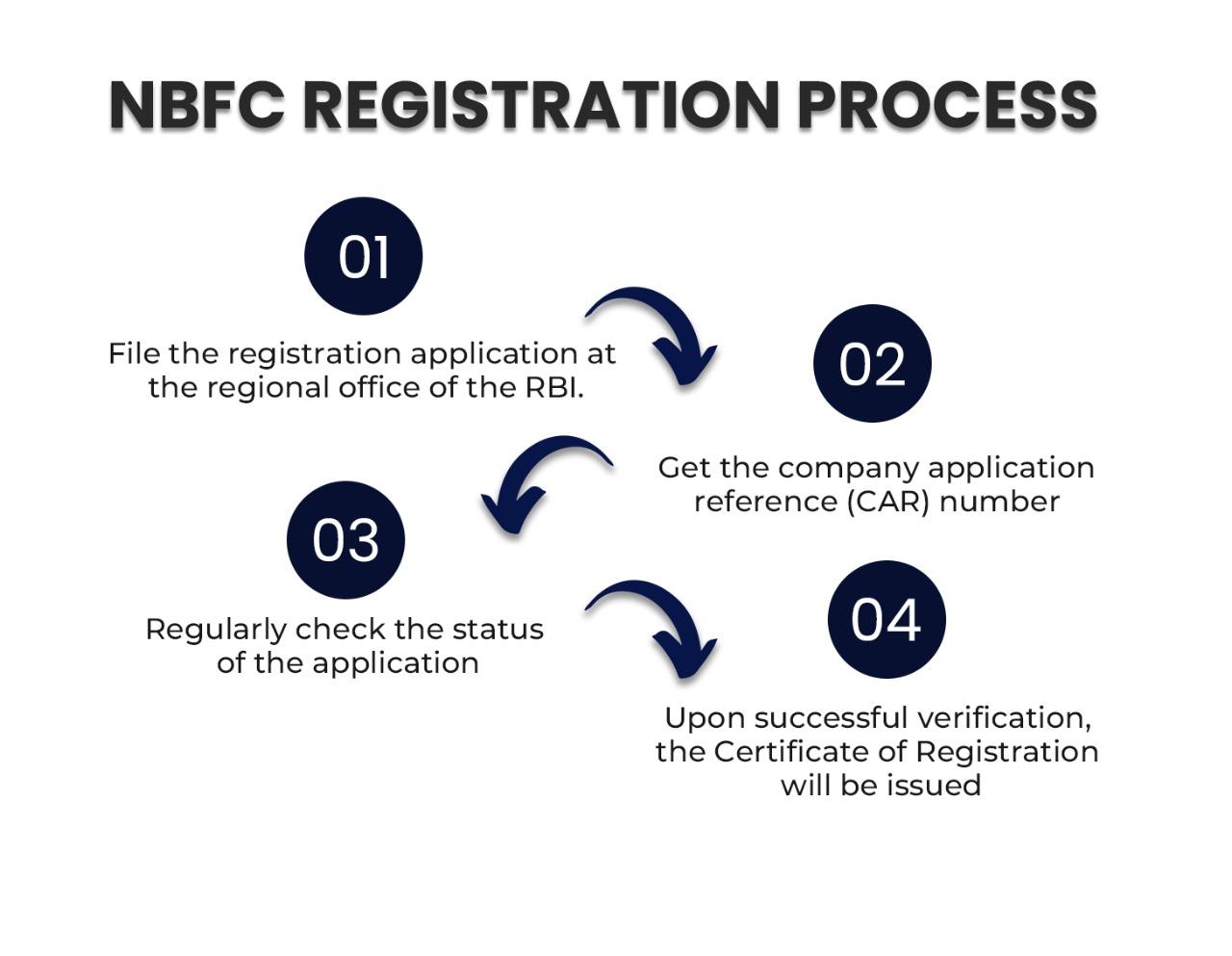
The required processing fee for the NBFC registration of a license is approximately Rs. 3, 50,000 to register a company as NBFC with a Net Owned Fund of Rs. 10 crores. If you are opting for the professional expertise of an NBFC consultant, you have to additionally pay 10-12 lakhs rupees. Therefore, the total expenditure for you to procure an NBFC license could amount to Rs. 15-16 lakhs
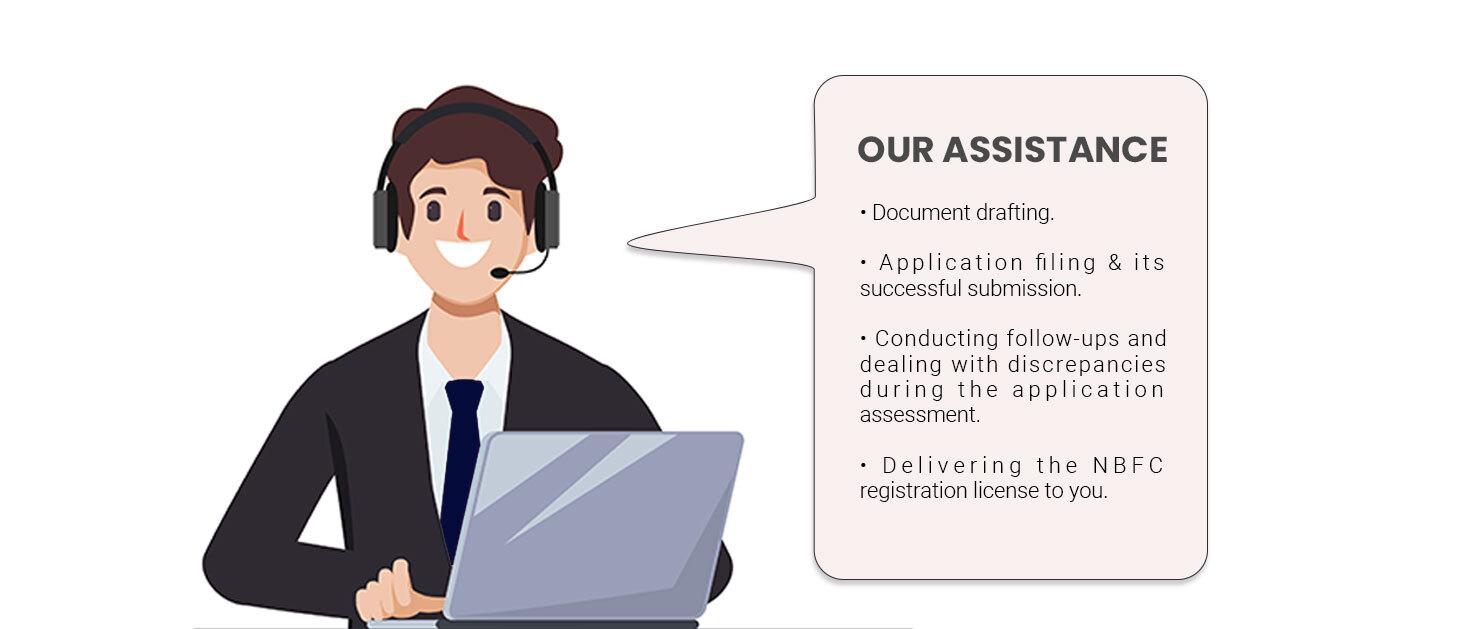
Registrationwala can assist you with the NBFC license registration for your business by providing you with the following services:
So, connect with us if you want the NBFC Registration for your company in a time and cost-effective manner.
A. It is a legal permit issued by the RBI authorizing its license holder to commence or
resume its Non-Banking financial services to its clients/customers.
A. Yes. The NBFCs are regulated under the RBI act of 1934.
A. An NBFC must be a registered company under the Companies Act and
must have a net owned fund of INR 10 crores.
A. The list of registered NBFCs is available on the website of the Reserve Bank of India
and can be viewed at www.rbi.org.in → Sitemap → NBFC List.
Q.5) How does one define a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC)?
A. A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 which engages in the business of

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
I very much appreciate the fact that you guys possess tremendous knowhow of private limited company incorporation. You have exhibited professional and respectful manner towards my query and I would seriously recommend you guys to all the folks looking for outstanding business services.

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
Thanks to their support, I got my trademark successfully. I highly recommend their services for anyone needing help with their intellectual property. The person assigned to me was very cooperative and helpful.

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
Thanks to their support ragistrationwala team, I got my IP-1 license successfully and special thanks to Miss.Kanishka for your great and timing support !!!!!! I have archived my goal one step forward... Thanks for the entire team....

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
Really helped a lot in getting my both VNO licenses. Great experience working with the team and very humble team, thanks for providing the vno license on time.

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
I had a good time working with Registrationwala. Good team. I would recommend their services to others.

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
It was extremely great service of Registrationwala consulting firm, and this firm is providing the best services and worry about the client's required services along the client's satisfaction.

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
Superb Experince! Within no time the trademark registration was on.Highly professional team. I am very much Impressed with the prompt response and efficiency.Thank you.

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
We had taken ISP license from registration wala and the supporting person is very helpful to taken that license his communication and his work is satisfactory and thanks for those services

★ ★ ★ ★ ★
I sincerely appreciate your prompt support in helping me get the access license so quickly. Your professionalism and efficiency are truly commendable. Thank you for going above and beyond to assist me. Keep up the great work!